【R】2標本のt検定
2020年4月16日
架空の話として。。。
都市Aと都市BでPM2.5(微小粒子状物質)の1日の平均観測量を比べた時に、両都市でPM2.5の飛散量に差があるかどうかを以下の手順で検証します。
①架空のデータを作ります。
②ヒストグラムでデータを確認します。
③シャピロ・ウィルクの検定で正規性を確認します。
④分散性を確認します。
⑤t検定します。
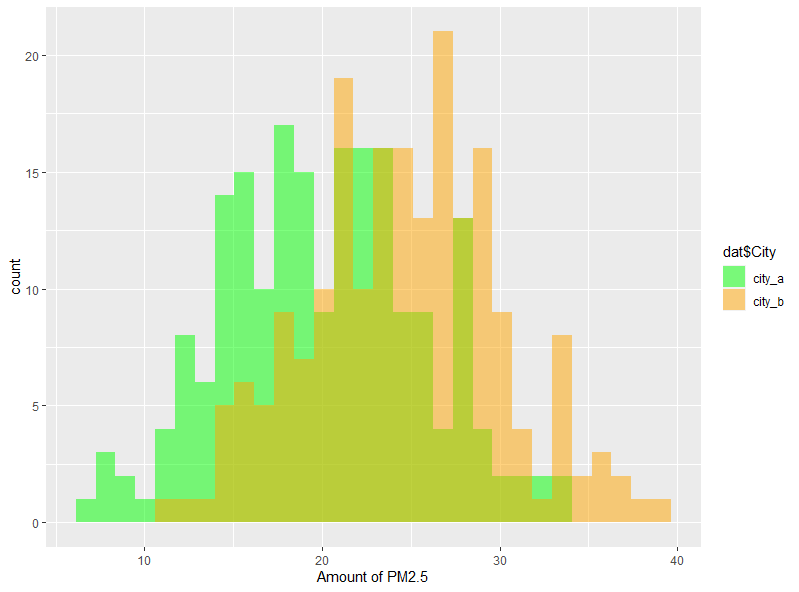
⑥2つのヒストグラムを重ねて表示します。
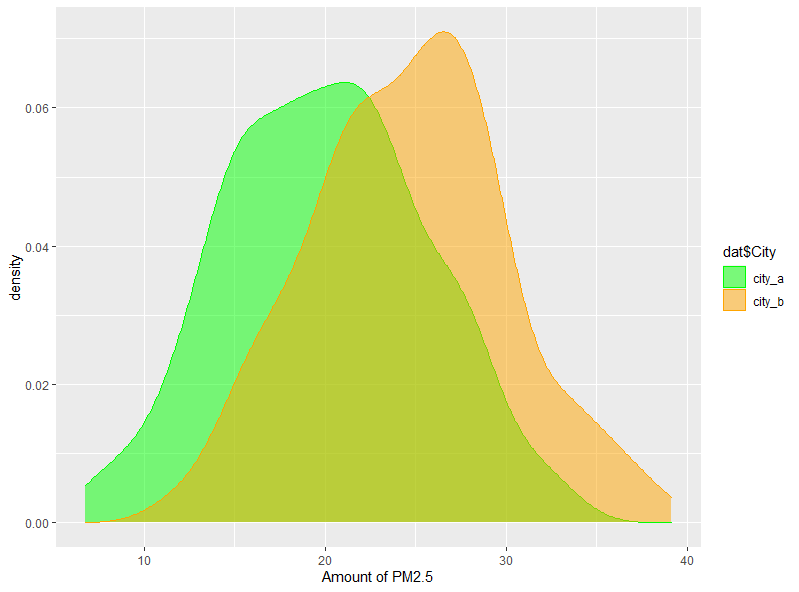
⑦2つのデータを密度プロットしてみます。
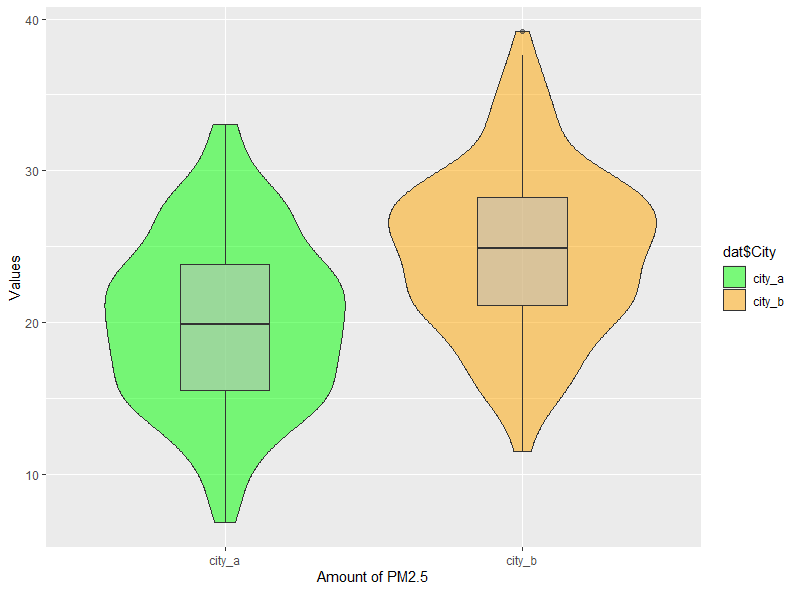
⑧バイオリンプロットとボックスプロットでも表示してみます。
#データ生成・・・① city_a <- rnorm(n=200, mean=20, sd=5.1) #正規分布の架空データ 都市AのPM2.5飛散量 city_b <- rnorm(n=200, mean=25.3, sd=5.4) #正規分布の架空データ 都市BのPM2.5飛散量 #ヒストグラムで確認・・・② layout(matrix(1:2, 1, 2)) hist(city_a, breaks=seq(0,50,2.5), xlab="range", xlim=c(0,50), ylim=c(0,50)) hist(city_b, breaks=seq(0,50,2.5), xlab="range", xlim=c(0,50), ylim=c(0,50))

何となく正規分布してそうですが、検定にて確認します。
# 正規性の検定・・・③ shapiro.test(city_a) shapiro.test(city_b)
> shapiro.test(city_a) Shapiro-Wilk normality test data: city_a W = 0.99264, p-value = 0.4147 > shapiro.test(city_b) Shapiro-Wilk normality test data: city_b W = 0.99426, p-value = 0.6389
帰無仮説は棄却されませんので、帰無仮説(正規分布でないとはいえない)を採択して、データは正規分布であるとします。次に、2標本の母分散が等しいかどうかを確認します。
#分散性の検定・・・④ var.test(city_a, city_b)
結果を見ますと、帰無仮説(分散は等しい)が棄却されなかったので、分散はひとしいとします。
> var.test(city_a, city_b)
F test to compare two variances
data: city_a and city_b
F = 1.0263, num df = 199, denom df = 199, p-value = 0.8548
alternative hypothesis: true ratio of variances is not equal to 1
95 percent confidence interval:
0.7767039 1.3561528
sample estimates:
ratio of variances
1.026318
分散が等しいとして、t検定をします。
#t 検定・・・⑤ t.test(city_a, city_b, var.equal = T)
Two Sample t-test data: city_a and city_b t = -8.3495, df = 398, p-value = 1.147e-15 alternative hypothesis: true difference in means is not equal to 0 95 percent confidence interval: -5.671072 -3.509467 sample estimates: mean of x mean of y 20.05004 24.64030
この結果、2つの都市で差があるといえます。
続いて、2標本をいろいろなプロットで表示してみます。
dat_a<-data.frame("City"=c(rep("city_a", length(city_a))), "Val"=city_a)
dat_b<-data.frame("City"=c(rep("city_b", length(city_b))), "Val"=city_b)
dat<-rbind(dat_a, dat_b)
# 2つのヒストグラムをまとめて表示・・・⑥
library(ggplot2)
ggplot(dat) + #データフレーム指定
geom_histogram(aes(x=dat$Val, fill=dat$City), #描画対象の変数
position="identity", #重ねて描画
alpha=0.5,
bandwidth=2) +
scale_fill_manual(values=c("green", "orange")) +
labs(x="Amount of PM2.5")
# 都市で色分けして密度プロットを描く・・・⑦
ggplot(dat) + #データフレーム指定
geom_density(aes(x=dat$Val,
color=dat$City,
fill=dat$City),
alpha=0.5) +
scale_color_manual(values=c("green", "orange"))+
scale_fill_manual(values=c("green", "orange"))+
labs(x="Amount of PM2.5")
# バイオリンプロットとボックスプロットを重ねて描く・・・⑧
ggplot(dat) + #データフレーム指定
geom_violin(aes(y =dat$Val,
x =dat$City,
fill=dat$City),
alpha=0.5) +
geom_boxplot(aes(y =dat$Val,
x =dat$City),
fill="grey",
width=0.3,
alpha=0.5) +
scale_color_manual(values=c("green", "orange"))+
scale_fill_manual(values=c("green", "orange"))+
labs(x="Amount of PM2.5", y="Values")